
Frauds have become a part of everyday life in Sri Lanka. As an Audit Firm in Sri Lanka, we believe that it is our duty help fellow businessman. In the below article, I’m evaluating applicability of fraud triangle theory in Sri Lanka.
In 1973, Donald Cressey published the results of his research on embezzlement in Other People’s Money: A Study in the Social Psychology of Embezzlement. Mr. Cressey’s hypothesis has become known to many as the “fraud triangle.” This theory is more than 40-year-old. Is it still valid today in ever changing Sri Lankan context?
Yes, though the fraud triangle is decades old, the theory is still very real in Sri Lankan society today.
The fraud triangle outlines three components that contribute to increasing the risk of fraud; opportunity, pressure, and rationalization
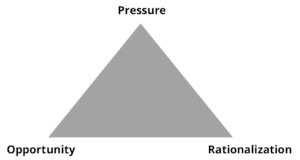
Opportunity
Opportunity refers to circumstances that allow stakeholder to engage in fraudulent activities. In the fraud triangle, it is the only component that a company a control. Weak internal control systems, poor tone from the top, inadequate accounting practices are some of the main reasons for creating opportunities for employees, customer and supplier to engage in fraudulent activities.
Due to lack of knowledge of small businessman and entrepreneurs in Sri Lanka regarding internal controls and accounting practices, it creates opportunities for employees to engage in fraudulent activities. Being an experienced audit firm in Sri Lanka we take pride in ourselves for providing consulting services to small and medium businessman to establish internal control, set the right tone at the top and implementing correct accounting practices.
Pressure
Pressure or incentive refers to the motivation or reason to commit the fraud. Examples include financial distress, drug or gambling addiction, or the desire to maintain a lavish lifestyle. Pressure or incentives for employees commit frauds increase during financially difficult and uncertain time periods. In Sri Lanka, we are currently going through a similar time period due to easter bomb attack and COVID 19 lockdown.
As a small and medium businessman, it difficult to impact this aspect of the fraud triangle. However, it is important to keep track of possible pressures behind employees in high-risk areas such as cashiers, procurement officers etc.
Rationalization
Rationalization refers to an individual’s justification for committing fraud. Individuals invents a story that makes it seem fair or reasonable to commit frauds. The justification is what allows the offender to commit and keep the fraud going over a long period of time. Some of these justifications include “owner treated me wrong”, “no other solution”, “owner is doing well but it’s my effort”, “I was not promoted” etc. These kinds of rationalizations allow, the offender not to feel guilt or remorse. Rationalization is a psychological state that’s very difficult to for owners. Rationalization side of fraud is very difficult to detect and prevent. But a healthy working environment with reasonable salary is the best option for mitigating fraud risk.
Article By – Sithira Ranwatta
